low end tidal co2 pulmonary embolism
Decreased perfusion to the lungs and reflex hyperventilation to compensate decreases end-tidal CO2 or ETCO2 5. Identifying potentially reversible causes during resuscitation from cardiac arrest is challenging 1.

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
This is result of a slower expiration.

. High VT and low resp rates. We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO 2 etCO 2 and tested two hypotheses. Arterial to end-tidal partial pressure of carbon dioxide Pa-Et CO 2 gradient may be useful in the evaluation of PE.
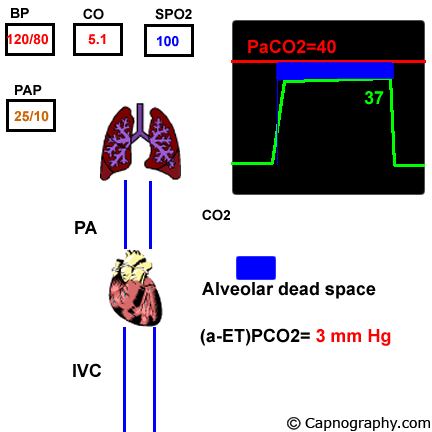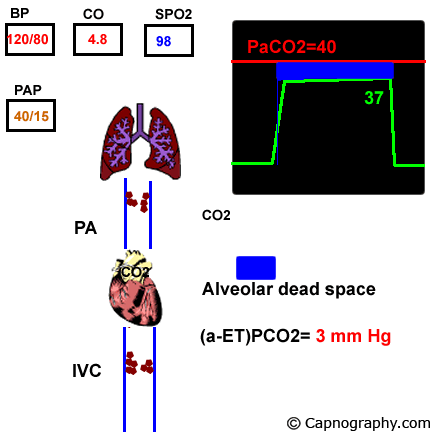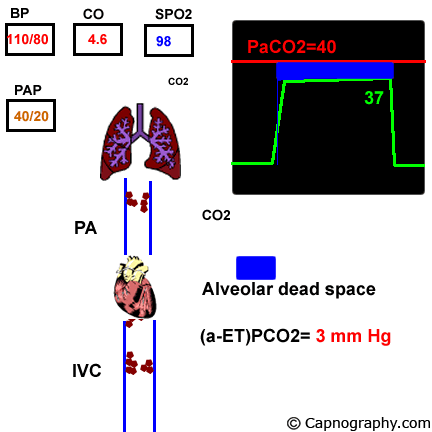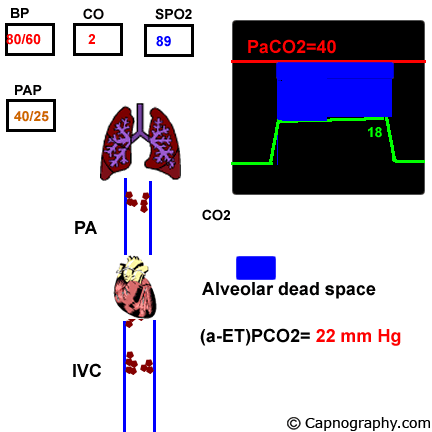
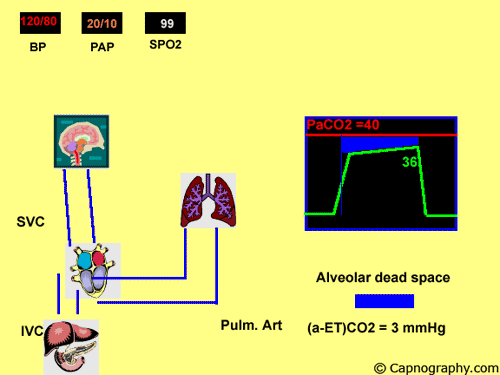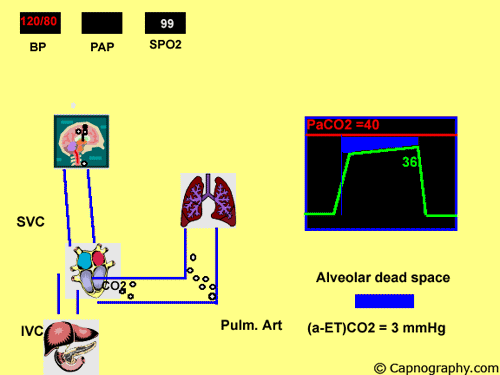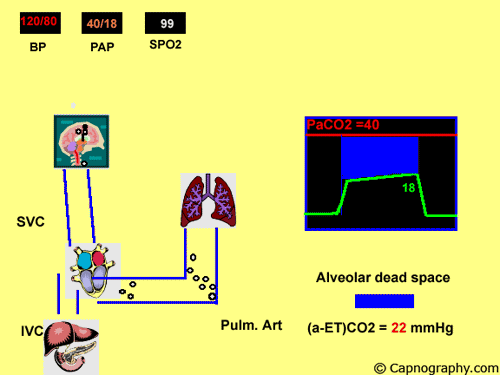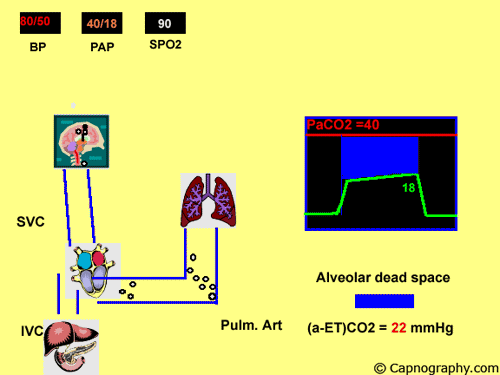
Pulmonary embolism increases alveolar dead space resulting in low end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 relative to arterial CO 2 PaCO 2 tension. End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 can represent dead space ventilation. Several studies have reported that computed tomography pulmonary angiography is the best method for diagnosing pulmonary embolism PE.
Pulmonary embolism PE is associated with approximately 100000 deaths per year in the United States and the incidence of deep vein thrombosispulmonary embolism in the United States is estimated at more than 350000 cases annually. Drummond et al3 defined the relative sensitivities of end tidal carbon dioxide analysis end-tidal nitrogen analysis and pulmonary artery pressure PAP monitoring in detection of venous air embolism VAE in a study. Low end tidal CO2 PetCO2 combined with normal arterial CO2 PaCO2 is suggestive of Pulmonary embolism The heart shadow should not occupy more than how much of the total transthoracic space.
A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is often missed. Thus a low EtCO 2 PaCO 2 ratio during resuscitation may be a sign of pulmonary embolism.
A low ETCO2 reading or hypocapnea can be caused by other respiratory conditions. This was a prospective diagnostic study set in a British acute medical admissions wardPatients suspected of having a. We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO2 etCO2 and tested two hypotheses.
Deeper slower alveoli are able to share their gas with the capnometer whereas previously that gas would have remained in the airway. Ad Get Info On An Rx Option To Treat Lower The Risk Of Recurrent DVTPE Blood Clots. A low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism Introduction.
Therefore in the event of a rapid decrease in PETCO2. CTPA computed tomography pulmonary angiogram. Sudden decrease or loss of end-tidal CO2 suggests a drastic decrease in cardiac output due to gas embolism.
The authors aimed to define the optimum ETCO2 to conclusively exclude a pulmonary embolic event. End tidal CO2 revealing a substantially low CO2 measurement also suggests hypocapnia eg etCO2. This study however aimed to predict or exclude PE using the end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 value and alveolar dead space fraction AVDSf together.
However this may also be caused by pulmonary dysfunction with an increase in dead space volume. Sudden decrease or loss of end-tidal CO2 suggests a drastic decrease in cardiac output due to gas embolism. Download Support Resources For DVTPE Find Tips To Help You Talk To Your Doctor.
At a cut-off of 36 mmHg capnography achieved a negative predictive value of 966. This figure shows that no patient with an ETCO2 3253 had a pulmonary embolism. Why Is End-tidal Co2 Low.
Where the respiratory rate is very low and the tidal volumes are very large the end-tidal CO 2 can be higher than the mean arterial CO 2. Therefore correlation between the end tidal CO2 and an ABGVBG measurement is needed to confirm the diagnosis of hypocapnia. In a similar larger study of 298 patients Hemnes et al.
A blocked pulmonary artery causes less CO2 to return to the lungs and less CO2 is released from the body as a result. One hundred consecutive patients with suspected pulmonary embolisms PEs were enrolled over 6 months in 2012. Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which leads to low ETco 2.
Riaz I Jacob B Pulmonary embolism in Bradford UK. To evaluate whether EtCO2 measurement can be used at the bedside to exclude pulmonary embolism PE. A reduced cardiac output by itself can decrease PETCO2.
One-hundred patients were included in the present. Continuous pulmonary arterial pressure can be used to evaluate for gas embolism. Management of a suspected CO2 embolism begins with desufflation of the abdomen.
In the group of patients finally diagnosed with PE n 39 end-tidal CO 2 was significantly lower than in the group without PE or in healthy volunteers. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism PE because of nonspecific clinical presentation remains as a challenge for emergency physicians. Underwent ETCO2 determination within 24 hours of diagnostic imaging 19.
The line represents a threshold of 3253 mmHg. Because pulmonary embolism obstructs pulmonary blood vessels not the airways. End-tidal carbon dioxide tension P ETCO 2 is a physiological surrogate for vascular obstruction from PE.
We performed a post hoc analyses of data from two prospective. This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time resulting in overdistention or from such circulatory problems as. When ETCO2 is low think of perfusion metabolic or psychological problems.
Continuous pulmonary arterial pressure can be used to evaluate for gas embolism. 1 that etCO2 can distinguish massive PE from hemorrhagic shock and 2 that PE with cardiac arrest reduces etCO2 during resuscitation to a greater extent than arrhythmic cardiac arrest. 1 The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism poses a diagnostic challenge in the emergency department ED despite.
End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status. ETCO2 end-tidal carbon dioxide. Role of end-tidal CO2 as a screening tool Clin Med.
Symptoms demographic date Wells score D-dimer levels and the gold standard computed. Pulmonary thromboembolism results in dead space ventilation and therefore prevents meaningful gas exchange in the subtended lung unit yielding an alveolar CO 2 content as low as 0. All study participants underwent end-tidal CO 2 determination within 24 h of state-of-the-art diagnostic imaging.
1 that etCO 2 can distinguish massive PE from hemorrhagic shock and 2 that PE with cardiac arrest reduces etCO 2 during resuscitation to a greater extent than arrhythmic cardiac arrest.

Pulmonary Embolism And Gas Exchange Semantic Scholar

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography And Pulmonary Embolism Chapter 21 Capnography

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

Basics Of Waveform Capnography Waveform Capnography Grepmed

Capnogram With Progressive Decline In Etco2 Generally Associated With Download Scientific Diagram

Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram

Bedside Investigation Of Pulmonary Embolism Pe Diagnosis Predictors Download Scientific Diagram

Bedside End Tidal Co2 Tension As A Screening Tool To Exclude Pulmonary Embolism European Respiratory Society

Rishi Kumar Md A Capnogram S Shape Provides Insight About Pulmonary Obstruction And Compliance The Difference Between Arterial Co2 Paco2 And End Tidal Co2 Etco2 Relates To Alveolar Dead Space Changes In Metabolism

A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation

Pre Hospital Capnography Ppt Download

Evaluation Of Suspected Pulmonary Embolism Utilizing End Tidal Co2 And D Dimer The American Journal Of Surgery

Figure 1 From Pulmonary Embolism Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment Semantic Scholar

Flow Diagram Of The Study Pet Co2 End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Tension Download Scientific Diagram